Genetic Research of the Iranian Plateau
Since 2021, the Institute of Archaeogenomics has been collaborating with the Noor Human Genetics Center in Tehran and the Cultural Heritage Office of Tehran on bioarchaeological research at various prehistoric and historic sites in Iran. Our main research questions include: To what extent was there population continuity or change in the Zagros region during the Chalcolithic period? What were the origins of the populations inhabiting northern Iran during the Achaemenid, Parthian, and Sasanian Empires? What kind of connections did these populations have with the peoples of Central Asia and the Caucasus region? How did the Silk Road, which passed through the northern Iranian Plateau, and the dynamic trade networks stretching east and west influence the biological composition of the populations living along the trade routes? An additional topic of our research focuses on the genetic composition of modern populations in Iran, which we summarize through a review of literature data.
The Institute of Archaeogenomics is responsible for conducting genetic analyses in this research, while our Iranian archaeologist and anthropologist partners contribute by performing anthropological analyses of human remains and providing archaeological context to support joint interpretations.
Planned timeframe of the project: 2021–2025
Project leader: Anna Szécsényi-Nagy
Host institute: Institute of Archaeogenomics, HUN-REN Research Centre for the Humanities
Participating researchers of the project:
- Motahareh Ala Amjadi
- Balázs Egyed (ELTE)
- Dr. Mahmoud Tavallaei, Dr. Maryam Ramezani (NHGRC)
- Yusuf Can Özdemir, Balázs G. Mende (HUN-REN RCH IAG)
Publications of the research results:
- Motahareh Amjadi, Maryam Ramezani, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Balázs Egyed, Mahmood Tavallaie, Abdol Motalleb Sharifi, Farzad Forouzanfar:
Following the traces of Parthians at the Vastmin archaeological site in Iran. Oral presentation at the 28th EAA Annual Meeting, Budapest, Hungary, 31 August – 3 September 2022 - Motahareh Amjadi, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Mahmood Tavallai, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Maryam Ramezani, Balázs Egyed, Farzad Forouzanfar, Zeinab Salehi, Arezoo Bibak, Peyman Zargari, Abdol Motalleb Sharifi, Ata Hasanpour, Vali Jahani:
Parthians of the Forgotten Empire. Oral presentation at the 5th international and 17th Iranian Genetic Congress, Tehran, Iran, 6–8 March 2023, https://gc2023.ir - Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Ancient DNA records from Western Asia: State of research on prehistoric palaeogenetics. 5th international and 17th Iranian Genetic Congress, Tehran, Iran, 6–8 March 2023, https://gc2023.ir - Motahareh Amjadi, Maryam Ramezani, Kristóf Jakab, Balázs G. Mende, Abdol Motalleb Sharifi, Ata Hasanpour, Vali Jahani, Arezoo Bibak, Mahmood Tavallaie, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Genomic analyses of Seleucid and Parthian period population in North Iran. Poster presented at the 10th Meeting of the International Society for Biomolecular Archaeology (ISBA), Tartu, Estonia, 13–16 September 2023 - Motahareh Amjadi, Zahra Hayatmehr, Balázs Egyed, Mahmood Tavallaei, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
A comprehensive review of HVS-I mitochondrial DNA variation of 19 Iranian populations. Annals of Human Genetics 2024; 88(3): 259-277. https://doi.org/10.1111/ahg.12544 - Motahareh Amjadi, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Mahmood Tavallai , Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Maryam Ramezani, Balázs Egyed, Kirstóf Jakab, Arezoo Bibak, Zeinab Salehi, Farzad Forouzanfar, Peyman Zargari, Parastoo Erfanmanesh, Ata Hasanpour, Vali Jahani, Seyed Mansour Seyed Sajjadi, Hossein Moradi, Ali Mahfroozi, Serollah Ghasemi Gorji, Abdol Motalleb Sharifi, Lili Niakan, Mohammad Hossein Taheri, Arman Shishegar:
Exploring Iran Genetic Past: Investigating Ancient Migrations through Skeletons. Oral presentation at the 6th International and 18th Iranian Genetic Congress, Shahid Beheshti University, Tehran, Iran, 7–9 July 2024 - Motahareh Ala Amjadi, Yusuf Can Özdemir, Maryam Ramezani, Kristóf Jakab, Melinda Megyes, Arezoo Bibak, Zeinab Salehi, Zahra Hayatmehar, Mohammad Hossein Taheri, Hossein Moradi, Peyman Zargari, Ata Hasanpour, Vali Jahani, Abdol Motalleb Sharifi, Balázs Egyed, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Mahmood Tavallaie, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Ancient DNA indicates 3,000 years of genetic continuity in the Northern Iranian Plateau, from the Copper Age to the Sassanid Empire, Nature Scientific Reports 15, 16530 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-99743-w - Yusuf Can Özdemir:
Ancient DNA indicates 3,000 years of genetic continuity in the Northern Iranian Plateau, from the Copper Age to the Sassanid Empire. Oral presentation at the 3rd ATES Open Science Conference, Budapest, 9 September 2025
Complex analyses of the Late Copper Age burials in the Carpathian Basin
 The team of the NKFIH K-18/128413 research project is led by Mária Bondár (IA RCH HAS). The Carpathian Basin was often the core territory of major cultural complexes and it also acted as a mediating or transit region in prehistoric periods. The archaeological record thus preserves evidence of contacts with diverse regions, whose vestiges can be found in the grave inventories too. Only a small portion of the customs and rites associated with the mortuary domain can be identified using archaeological methods. When archaeologists uncover a grave, they find human remains in various states of preservation. They can document the location of the burial, the grave pit, and the artifacts, as well as the various dimensions of the burials (the choice of burial location, the imprints of rituals, artifacts articulating status and social prestige), all of which reveal much about the position of the individual in the community and his/her cultural and other contacts (ancestry, place of origin, trade, etc.) as well as about the community's beliefs and attitudes to death. The remains preserve the biological condition of the once-living person (inherited traits, environmental influences, health). The overall goal of the project is a complex assessment of the period's burials combining archaeological and archaeometric analyses, and the integration of the findings in order to identify the differences between individuals interred according to widely differing mortuary practices through an examination of the biological social, and cognitive dimensions of funerary customs. Moreover, the research project is also a useful exercise for determining to what extent the application of these analytical procedures can provide meaningful data about prehistoric communities that left no literary records.
The team of the NKFIH K-18/128413 research project is led by Mária Bondár (IA RCH HAS). The Carpathian Basin was often the core territory of major cultural complexes and it also acted as a mediating or transit region in prehistoric periods. The archaeological record thus preserves evidence of contacts with diverse regions, whose vestiges can be found in the grave inventories too. Only a small portion of the customs and rites associated with the mortuary domain can be identified using archaeological methods. When archaeologists uncover a grave, they find human remains in various states of preservation. They can document the location of the burial, the grave pit, and the artifacts, as well as the various dimensions of the burials (the choice of burial location, the imprints of rituals, artifacts articulating status and social prestige), all of which reveal much about the position of the individual in the community and his/her cultural and other contacts (ancestry, place of origin, trade, etc.) as well as about the community's beliefs and attitudes to death. The remains preserve the biological condition of the once-living person (inherited traits, environmental influences, health). The overall goal of the project is a complex assessment of the period's burials combining archaeological and archaeometric analyses, and the integration of the findings in order to identify the differences between individuals interred according to widely differing mortuary practices through an examination of the biological social, and cognitive dimensions of funerary customs. Moreover, the research project is also a useful exercise for determining to what extent the application of these analytical procedures can provide meaningful data about prehistoric communities that left no literary records.
Partner institute: HAS, Research Centre for Astronomy and Earth Sciences, Institute for Geological and Geochemical Research
Participants of the project: Zoltán Kern, János Jakucs, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Ariana Gugora, Kitti Köhler, Erika Gál, István Hegyi, Krisztián Oross, Attila Demény, Enikő Lajtár, Piroska Rácz, Dániel Gerber, Tibor Marton
Publications of the research results:
- Dániel Gerber, János Jakucs, Piroska Rácz, Krisztina Somogyi, Szilvia Honti, Balázs G. Mende, Mária Bondár, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Interdisciplinary analyses of Late Copper Age cemeteries from southern Transdanubia – 28th EAA Annual Meeting, Budapest, 2022.08.31–09.03. - Gerber Dániel: Balatonszentgyörgy-Faluvégi dűlő 2. lelőhely emberi maradványainak genetikai analízise. In: Bondár Mária - Somogyi Krisztina (szerk.): Késő rézkori birituális temető Balatonszentgyörgy határában. Budapest, Magyarország: Archaeolingua Alapítvány, MTA BTK Régészeti Intézet (2022), 293–295. ISBN: 9786155766558.
- Gunnar U. Neumann, Aida Andrades Valtueña, Maria A. Spyrou, Lyazzat Musralina, Sandra Penske, Anja Furtwängler, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Dániel Gerber, Mária Bondár, Piroska Rácz, Adela Sobotkova, Katharina Rebay-Salisbury, Fabian Kanz, Philipp W. Stockhammer, Johannes Krause, Wolfgang Haak, Alexander Herbig:
Early diversity and evolution of Yersinia pestis from the late Neolithic and Bronze Age, EMBO/EMBL Symposium “Reconstructing the Human Past” Heidelberg, Németország, 13–16 September 2022 - Gerber Dániei:
Az archeogenetikai vizsgálatok múltja, jelene és jövője Magyarországon. Késő rézkori temetkezések régészeti és bioarcheológiai elemzése. HTK Budapest 2023.12.14. - Gerber Dániel:
Az archeogenomikai vizsgálatok múltja, jelene és jövője Magyarországon (English abstract: Archaeogenomic studies in Hungary. Past, present and future). In: Bondár Mária (szerk.): Késő rézkori temetkezések régészeti és bioarcheológiai elemzése (Archaeological and Bioarchaeological Studies on Late Copper Age Burials), Budapest 2023, pp. 557-590. ISBN: 978-615-5766-64-0. https://doi.org/10.62150/BM.KRT.2023_11
Árpád dynasty program: The anthropological and genetic composition of the Árpád Age Hungarian population (V.1 subproject)
Leader of the consortium: Dr. Zoltán Korsós (Hungarian Natural History Museum)
Duration of the project: 2018-2023
Collaborating institutions: Hungarian Natural History Museum, Institute of Archaeology RCH, University of Szeged
Objectives of the Institute of Archaeology RCH within the project: genetic investigation of the 7-13th century populations of the Carpathian Basin
 The project intends to lay modern tools for a comprehensive anthropological and genetic examination of the population of the Árpád-era Carpathian Basin, including the sampling of 10-13 individuals living in the country of Árpád ages. We planning to analyze these samples with natural science methods and laboratory instruments of the currently known international level. The primary task is the complex osteoarcheological and comparative genetic examination (continuity and discontinuity) between samples spring from 8-13. centuries (avar age, conquest age, and Árpád era). This population has the historically highest importance in this field. Sampling is based on recommendations of anthropologists, archaeologists, historians and aimed at the widest genetic characterization of the groups, which may respond to archaeological-historical contexts. To this end, the project aims to achieve an anthropological database, domestic and international conferences and publications, the implementation of a Hungarian project closing book. Goals of the project in Institute of Archeogenomics: the Carpathian Basin in 7-13. century genetic examination of the populations.
The project intends to lay modern tools for a comprehensive anthropological and genetic examination of the population of the Árpád-era Carpathian Basin, including the sampling of 10-13 individuals living in the country of Árpád ages. We planning to analyze these samples with natural science methods and laboratory instruments of the currently known international level. The primary task is the complex osteoarcheological and comparative genetic examination (continuity and discontinuity) between samples spring from 8-13. centuries (avar age, conquest age, and Árpád era). This population has the historically highest importance in this field. Sampling is based on recommendations of anthropologists, archaeologists, historians and aimed at the widest genetic characterization of the groups, which may respond to archaeological-historical contexts. To this end, the project aims to achieve an anthropological database, domestic and international conferences and publications, the implementation of a Hungarian project closing book. Goals of the project in Institute of Archeogenomics: the Carpathian Basin in 7-13. century genetic examination of the populations.
Colleagues working on this project: Elek Benkő (IA RCH), Szabina Merva (IA RCH), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH), Anna Szécsényi-Nagy (IAG RCH), Bea Szeifert (IAG RCH, ELTE), Dániel Gerber (IAG RCH, ELTE)
Publications of the research results:
- Veronika Csáky, Bea Szeifert, Dániel Gerber, Béla Szőke, Szabina Merva, Sándor Évinger, Csilla Líbor, Zsolt Petkes, Balázs Mende, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
The issue of continuity of population history between 8-12th centuries in Carpathian Basin based on archaeogenetic results of four cemeteries – 28th EAA Annual Meeting, Budapest, Hungary, 31 August – 3 September 2022 - Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Veronika Csáky, Noémi Borbély, Dániel Gerber, Balázs Gyuris, Kristóf Jakab, Bea Szeifert, Balázs G. Mende:
Genetic formation and structure of the early Hungarian Kingdom’s population based on whole genome data – EMBO/EMBL Symposium “Reconstructing the Human Past” Heidelberg, Germany, 13–16 September 2022 - Szeifert Bea, Csáky Veronika, Gerber Dániel, Szőke Béla Miklós, Merva Szabina, Petkes Zsolt, Évinger Sándor, Rácz Piroska, Líbor Csilla, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna, Mende Balázs Gusztáv:
Dunántúli hatalmi központok Árpád-kori népességeinek bemutatása az új genetikai kutatások tükrében – Aranybulla 800, Budapest, Magyarország, 2022.10.10. - Petkes Zsolt, Csáky Veronika:
Egy nagyváros első lépései – Székesfehérvár területe a 10. században – ALBA REGIA – BULLA AUREA Régészeti és történeti perspektívák Székesfehérvár régmúltjának kutatásában, Tudományos konferencia 972, 1172, 1222 jubileuma alkalmából, Székesfehérvár, 2022.12.14 - Borbély Noémi, Csáky Veronika, Szeifert Bea, Gerber Dániel, Gyuris Balázs, Jakab Kristóf, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna:
Genetikai képek a Kárpát-medencéből: teljes genom elemzések a 9–12. századi Dunántúlról és az Árpád-kori székelység köréből – XXI. “Genetikai Műhelyek Magyarországon Minikonferencia” 2022, Szeged, Hungary, 2022.09.07. - Noémi Borbély, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Ron Pinhasi; Olivia Cheronet; David Emil Reich; Ágoston Takács, Tamás Hajdu, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Investigation of the genetic ancestry of Béla of Macsó, an Árpádian prince from Hungary – 28th EAA Annual Meeting, Budapest, Hungary, 2022.08.31–09.03. - Bea Szeifert, Balázs Gyuris, Kristóf Jakab, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Péter Langó, Attila Türk, Vitalij Sinika, Dániel Giedl, Péter Major, Norbert Berta, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Analysis of genetic connections between the medieval communities of the Dniester Valley and the Carpathian Basin. 10th Meeting of the International Society for Biomolecular Archaeology (ISBA), 13–16 September 2023, Tartu, Estonia - Szécsényi-Nagy Anna, Szeifert Bea, Gyuris Balázs, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Csáky Veronika, Langó Péter, Türk Attila:
Új genetikai adatok a honfoglalás kori népesség eredetéhez és biológiai kapcsolatrendszeréhez. Árpád népe – A magyar honfoglalás kor kutatásának legújabb eredményei, 2023. 04. 13. – 15. Szentendre, Hungary - Szeifert Bea, Gerber Dániel, Csáky Veronika, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Szőke Béla Miklós, Petkes Zsolt, Szücsi Frigyes, Major Péter, Giedl Dániel:
Betekintés a középkori Dunántúl lakosságának genetikai összetételébe. Kárpát-medence középkori és újkori népességeinek genetikai kutatása. BTK, Budapest, Hungary, 2023.12.12. - Bea Szeifert, Dániel Gerber, Veronika Csáky, Balázs Gyuris, Kristóf Jakab, Béla Szőke, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Vitalij Sinika, Attila Türk, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Genetic Makeup and Change in the Mediaeval Communities of the Carpathian Basin. EAA AM 2024 Rome, 27–31 August 2024. - Szeifert Bea, Gerber Dániel, Csáky Veronika, Gyuris Balázs, Jakab Kristóf, Szőke Béla Miklós, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Türk Attila, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna:
Csak a változás állandó? Genetikai adatok a középkori Kárpát-medence lakosságának összetételéről. Genetikai Műhelyek Magyarországon. HUN-REN Biological Research Centre, Szeged, Hungary, 2024.09.06. - Dániel Gerber, Veronika Csáky, Bea Szeifert, Noémi Borbély, Kristóf Jakab, György Mező, Zsolt Petkes, Frigyes Szücsi, Sándor Évinger, Csilla Líbor, Piroska Rácz, Krisztián Kiss, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Béla Miklós Szőke, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Ancient genomes reveal Avar-Hungarian transformations in the 9th-10th centuries CE Carpathian Basin. Sci. Adv. 10, eadq5864(2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adq5864 - Balázs Gyuris, Leonid Vyazov, Attila Türk, Pavel Flegontov, Bea Szeifert, Péter Langó, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Veronika Csáky, Andrey A. Chizhevskiy, Ilgizar R. Gazimzyanov, Aleksandr A. Khokhlov, Aleksandr G. Kolonskikh, Natalia P. Matveeva, Rida R. Ruslanova, Marina P. Rykun, Ayrat Sitdikov, Elizaveta V. Volkova, Sergei G. Botalov, Dmitriy G. Bugrov, Ivan V. Grudochko, Oleksii Komar, Alexander A. Krasnoperov, Olga E. Poshekhonova, Irina Chikunova, Dmitrii A. Stashenkov, Sergei Zubov, Alexander S. Zelenkov, Harald Ringbauer, Olivia Cheronet, Ron Pinhasi, Ali Akbari, Nadin Rohland, Swapan Mallick, David Reich & Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Long Shared Haplotypes Identify the Southern Urals as a Primary Source for the 10th Century Hungarians.
Human population genetics of the present-day Carpathian basin
 The fundamental task of this research is collecting approximately 300 human DNA samples from three regions of the Carpathian basin, where Hungarian-speaking communities live relatively isolated (Drávaszög/Baranja in Hungary and Croatia, area of Odorheiu Secuiesc in Romania and Zobor region in Slovakia). Our primary goal is to detect in these datasets old locally preserved maternal and paternal genetic lineages. We will type maternal lineages by sequencing 300 complete mitochondrial genomes, which will be one of the largest projects of this kind in Europe, using state-of-the-art technology. Testing approx. 100 Y chromosomes, we would like to gain insights into the natural diversity of the paternal gene pool of the three regions.
The fundamental task of this research is collecting approximately 300 human DNA samples from three regions of the Carpathian basin, where Hungarian-speaking communities live relatively isolated (Drávaszög/Baranja in Hungary and Croatia, area of Odorheiu Secuiesc in Romania and Zobor region in Slovakia). Our primary goal is to detect in these datasets old locally preserved maternal and paternal genetic lineages. We will type maternal lineages by sequencing 300 complete mitochondrial genomes, which will be one of the largest projects of this kind in Europe, using state-of-the-art technology. Testing approx. 100 Y chromosomes, we would like to gain insights into the natural diversity of the paternal gene pool of the three regions.
Our next research topic is the study of traits related to genetic origin and heritage on the autosomes, using cost-efficient microarray technology. The obtained genotypes allow statistical determination of genetic similarities or differences between several modern or between modern and ancient populations.
The further research area is the analyses of ancient mitogenomes from 60 medieval graves excavated in the surrounding villages of Odorheiu Secuiesc. We would study, how the maternal gene pool of the local population transformed from the Middle Ages to the present day.
With all of this, we aim to get to know the genetic composition of the populations in the Carpathian basin in geographical and historical context, but we do not wish to define or justify the "Hungarians" on a genetic basis. Project number: FK 127938 (NKFIH)
Project leader: Anna Szécsényi-Nagy
Participants of the project: Balázs Egyed (ELTE), Horolma Pamjav (NSZKK), Balázs G. Mende (AIG RCH), István Máthé (Sapientia), Noémi Borbély (IAG, RCH), Robert Selan (IAG, RCH)
Partner institutes of the project: Genetic Department of the ELTE University, Laboratory of Reference Samples Analysis in the Department of Genetics of the Directorate of Forensic Expertise in the Hungarian Institute for Forensic Sciences (HIFS), Sapienta Hungarian University of Transylvania, Constantine the Philosopher University in Nitra, Haáz Rezső Museum
Publications of the project:
High Coverage Mitogenomes and Y-Chromosomal Typing Reveal Ancient Lineages in the Modern-Day Székely Population in Romania
- Noémi Borbély, Bea Szeifert, Koppány Kerestély, Horolma Pamjav, Balázs Egyed, Zsolt Nyárádi, András Sófalvi, Szilárd Sándor Gál, Elek Benkő, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Investigating the archaic and modern-day székely gene pool around Székelyudvarhely – 28th EAA Annual Meeting, Budapest, Hungary, 2022.08.31–09.03. - Borbély Noémi, Csáky Veronika, Szeifert Bea, Gerber Dániel, Gyuris Balázs, Jakab Kristóf, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna:
Genetikai képek a Kárpát-medencéből: teljes genom elemzések a 9–12. századi Dunántúlról és az Árpád-kori székelység köréből – XXI. “Genetikai Műhelyek Magyarországon Minikonferencia” 2022, Szeged, Hungary, 2022.09.07. - Noémi Borbély, Koppány Kerestély, Elek Benkő, András Sófalvi, Zsolt Nyárádi, Horolma Pamjav, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Genetic study of modern and medieval Székely Land – Annual Meeting of Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, 2022.12.01. - Noémi Borbély, Orsolya Székely, Bea Szeifert, Dániel Gerber, István Máthé, Elek Benkő, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Balázs Egyed, Horolma Pamjav, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
High Coverage Mitogenomes and Y-Chromosomal Typing Reveal Ancient Lineages in the Modern-day Székely Population in Romania - Genes 2023, 14, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010133 [accepted on 27 December 2022] - Noémi Borbély, Horolma Pamjav, Balázs Egyed, István Máthé, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Uniparental genetic diversity of three Hungarian-speaking isolated communities in the Carpathian Basin. Haploid Markers 12, 2023.05.17–20. Budapest, Hungary - Noémi Borbély, Bea Szeifert, Elek Benkő, Dániel Gerber, Kristóf Jakab, Koppány Kerestély, András Sófalvi, Zsolt Nyárádi, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
Whole-genome data from three Hungarian-speaking minorities of the Carpathian Basin; Hungarian Molecular Life Sciences, 24–26 March, 2023, Eger, Hungary - Borbély Noémi, Pamjav Horolma:
Drávaszög és a Zobor vidék populációgenetikai vizsgálata. Kárpát-medence középkori és újkori népességeinek genetikai kutatása. BTK, Budapest, Hungary, 2023.12.12. - Szécsényi-Nagy Anna, Borbély Noémi, Benkő Elek, Sófalvi András, Nyárádi Zsolt:
Udvarhelyszék népességének genetikai összetétele a középkortól napjainkig. Kárpát-medence középkori és újkori népességeinek genetikai kutatása. BTK, Budapest,Hungary, 2023.12.12. - Pamjav H, Borbély N, Dudás D, Tapasztó A, Dudás-Boda E, Csáky V, Mende BG and Szécsényi-Nagy A:
Uniparental study of the Hungarian-speaking populations of Drávaszög and Zoboralja. XXII. “Genetikai Műhelyek Magyarországon” miniconference, 15 September 2023 - Borbély, Noémi, Orsolya Székely, Bea Szeifert, Dániel Gerber, István Máthé, Elek Benkő, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Balázs Egyed, Horolma Pamjav, and Anna Szécsényi-Nagy:
High Coverage Mitogenomes and Y-Chromosomal Typing Reveal Ancient Lineages in the Modern-Day Székely Population in Romania, Genes 14, no. 1 (2023): 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010133 - Noémi Borbély, Dániel Dudás, Attila Tapasztó, Eszter Dudás-Boda, Veronika Csáky, Bea Szeifert, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Balázs Egyed, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Horolma Pamjav:
Phylogenetic Insights into the Genetic Legacies of Hungarian-Speaking Communities in the Carpathian Basin. Sci Rep 14, 11480 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61978-4 - Borbély Noémi, Benkő Elek, Jakab Kristóf, Mező György, Sófalvi András, Nyárádi Zsolt, Heltai Botond, Megyes Melinda, Gál Szilárd Sándor, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna:
Whole-Genome Analysis of Medieval Székely People, Doctoral School of Biology Conference 2024, Budapest, Hungary, HUN-REN TTK, 2024.12.03. - Borbély Noémi, Benkő Elek, Sófalvi András, Nyárádi Zsolt, Heltai Botond, Megyes Melinda, Jakab Kristóf, Mező György, Gál Szilárd, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna:
Középkori székely minták genomikai elemzése székelyudvarhely régiójából. Genetikai Műhelyek Magyarországon. Biological Research Centre, Szeged, Hungary, 2024.09.06. - Noémi Borbély, Dániel Dudás, Attila Tapasztó, Eszter Dudás-Boda, Veronika Csáky, Bea Szeifert, Balázs Gusztáv Mende, Balázs Egyed, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Horolma Pamjav:
Phylogenetic Insights into the Genetic Legacies of Hungarian-Speaking Communities in the Carpathian Basin. Sci Rep 14, 11480 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61978-4
Molecular anthropological research for the Hungarian ethnogenesis
The aim of the molecular anthropological research launched within the framework of the Thematic Excellence Program won in 2019 is to research the history of the Hungarian people with scientific tools by examining both the populations living today and the archaeological human remains.
The research of the history of the Hungarian people is carried out in three complementary areas:
1. Archaeogenetic studies
The prehistory of the Hungarian people took place in a wide geographical environment, but we basically classify the finds to be examined into two large groups. On the one hand, it includes the legacies of populations belonging to all historical eras in the Carpathian Basin - including the times before and after the Hungarian conquest, as they are also considered to be the ancestors of the Hungarians living today - on the other hand, the legacies of the eastern migration of the conquering Hungarian tribes.
The aim of our molecular anthropology research group is to find answers to the basic questions of Hungarian ethnogenesis: to what extent the populations that have appeared, settled or migrated in the Carpathian Basin for centuries have participated in the formation of today's Hungarian people; how we relate to other European and Asian peoples; from which Eurasian areas did the peoples of the Hun, Avar and Hungarian conquest eras come to Hungary, and what ethnogenetic relationship do they have with each other and with other populations.
In the coming years we want to achieve new results in three stages of Hungarian ethnogenesis:
- We begin the study of the autochthonous population of the Carpathian Basin with the only cemetery with a large number of graves, which was already open before the Hungarian conquest and was in continuous use for almost three centuries: Halimba-Cseres, 9-12 century.
- We would like to continue the characterization of the genetic diversity of the conquering Hungarians by examining a region that has been left out of the research so far: Hungarian Conquering cemeteries of Heves county.
- We will start the genetic study of the later joined peoples with the only Árpádian-era Ishmaelite cemetery in the country: Orosháza-Bónum, Faluhely, 11-13 century.
Participants of the project: Fóthi Erzsébet (Institute of Archaeogenomics Research Centre of Humanities), Fóthi Ábel (IAG RCH), Makra Szabolcs (RCH IAG), Krizsik Virág (RCH IAG), Dudás Eszter (Hungarian Institute for Forensic Sciences), Évinger Sándor (Hungarian Natural History Museum), Madaras László (Damjanich János Museum), Szigeti Judit (Castle guardianship), Rózsa Zoltán (Castle guardianship), Balázs János (University Szeged, Department of Anthropology), Dóra Szegő (IAG RCH).
2. Recent population genetics
The aim of recent population genetic research is to compile a population genetic atlas of the Carpathian Basin. By genetic testing of today's populations, we want to create a population genetics database of the Hungarian-inhabited areas of the Carpathian Basin and eastern regions of origin of the conquering Hungarian tribes, which can serve as a reference not only in our own research group but also in other Hungarian and foreign scientific workshops. After the Bodrogköz, Rétköz, Csallóköz and Szeklers of Bukovina, the study of the genetic composition of new regions begins, including Heves county, Őrség and Sárrét.
Participants of the project: Erzsébet Fóthi (Institute of Archaeogenomics, Research Centre of Humanities), Ábel Fóthi (IAG RCH), Szabolcs Makra (IAG RCH), Virág Krizsik (IAG RCH), Pamzsav Horolma (Hungarian Institute for Forensic Sciences), Alexandra Kovács (IAG RCH).
3. Stable isotope analysis
The proportion of stable isotopes (C, N, O, and Sr) incorporated into the human body through nutrition provides an opportunity to study the diet and migration path of people in history.
The focus of the study was on the remains of the conquering Hungarians in the Carpathian Basin. By analyzing the findings of the Great Plain and the Upper Tisza region, we hope to obtain new data on the nutrition of the ancient Hungarians, the route and direction of their movement.
Participants of the project: Erzsébet Fóthi (Institute of Archaeogenomics, Research Centre of Humanities ), Attila Demény, and Ariana Gugora (Institute for Geological and Geochemical Research).
The Thematic Excellence Program is supported by the Ministry of Innovation and Technology (Commitment ID: ZH690024). The governing body is the National Research, Development, and Innovational Office (1121-1 / 2020).
Publications of the project:
- Ábel Fóthi, Virág Krizsik, Alexandra Kovács, Dóra Szegő, Horolma Pamjav, Ariana Gugora, Róbert Kaló, Balázs Könnyű, Bence Gálik, Péter Urbán, Attila Gyenesei, Erzsébet Fóthi:
Who spoke Hungarian here? A genetic comparison of ancient individuals with Uralic-speaking populations. – EMBO/EMBL Symposium “Reconstructing the Human Past” Heidelberg, Germany, 13–16 September 2022 - Fóthi Erzsébet, Dudás Dániel, Dudás Eszter, Tapasztó Attila, Kovács Alexandra, Fóthi Ábel, Horolma Pamjav (2022):
Bukovinai székelyek apai ági genetikai elemzése. – XXI. “Genetikai Műhelyek Magyarországon” miniconference, Szeged, Hungary, 9 September 2022 - Krizsik Virág, Fóthi Ábel, Szegő Dóra, Kaló Róbert, Könnyű Balázs, Gálik Bence, Urbán Péter, Gyenesei Attila, Fóthi Erzsébet:
Honfoglalás kori leletek uniparentális eredményei. – XXI. “Genetikai Műhelyek Magyarországon” miniconference, Szeged, Hungary, 9 September 2022 - Fóthi Ábel, Kovács Alexandra, Krizsik Virág, Szegő Dóra, Pamjav Horolma, Kaló Róbert, Könnyű Balázs, Gálik Bence, Urbán Péter, Gyenesei Attila, Fóthi Erzsébet:
Ma élő magyarok autoszomális elemzése – XXI. "Genetika Műhelyek Magyarországon" miniconference, Szeged, Hungary, 9 September 2022 - Pamjav, Horolma; Fóthi, Ábel; Dudás, Dániel; Tapasztó, Attila; Krizsik, Virág; Fóthi, Erzsébet:
The paternal genetic legacy of Hungarian-speaking Rétköz (Hungary) and Váh valley (Slovakia) populations - FRONTIERS IN GENETICS 13 Paper: 977517 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.977517 - Gugora, A; Demény, A; Fóthi, E ; Horváth, A ; Palcsu, L ; Karlik, M:
Detection of diagenetic alteration in bones and teeth for migration and dietary studies — a combined FTIR and C-N–O-Sr isotope study on tenth century CE cemeteries in northern and northeastern Hungary - ARCHAEOLOGICAL AND ANTHROPOLOGICAL SCIENCES 14 : 4 Paper: 58 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-022-01532-3 - Ábel Fóthi, Virág Krizsik, Alexandra Kovács, Dóra Szegő, Róbert Kaló, Horolma Pamjav, Ariana Gugora, Balazs Könnyű, Bence Gálik, Péter Urbán, Attila Gyenesei, Erzsébet Fóthi:
An admixture of people conquered the Carpathian basin in the 10th century. 10th Meeting of the International Society for Biomolecular Archaeology (ISBA), 13 –16 September 2023, Tartu, Estonia - Fóthi Ábel, Kovács Alexandra, Krizsik Virág, Szegő Dóra, Pamjav Horolma, Kaló Róbert, Könnyű Balázs, Gálik Bence, Gyenesei Attila, Urbán Péter, Fóthi Erzsébet:
Recens rétközi és bukovinai székely népesség uniparentális és autoszomális elemzése. Kárpát-medence középkori és újkori népességeinek genetikai kutatása. BTK, Budapest, 2023.12.12.
Eastern connections of the Hungarian Conquest period archaeological remains in context of the Hungarian prehistory
Archaeological database and archaeometric researches (OTKA -106369 project)
 The ancient Hungarians originated from the Ural region in today's central Russia and migrated across the Eastern European steppe, according to historical sources. The historically and linguistically assumed homeland of the ancient Hungarians was in the Central Ural region, which is an easily accessible part of the mountain range. The Finno-Ugric groups might have settled on both sides of the Urals during the early Medieval period. Archeological records, for example, from central-eastern Uralic site Uelgi, indicate an archaeological cultural mixture of northern Ugric and eastern steppic Turkic elements. These eastern components show cultural connections toward the region of the Emba River in today's western Kazakhstan and toward the Srostki culture, which indicates that the ancient Hungarian population could already have been reached in the Central Ural region by several cultural and genetic influences. Our laboratory studies the genetic composition of the people buried in 7-11th century cemeteries of the Ural region and compares the data with other 7-12th century DNA results from Eurasia.
The ancient Hungarians originated from the Ural region in today's central Russia and migrated across the Eastern European steppe, according to historical sources. The historically and linguistically assumed homeland of the ancient Hungarians was in the Central Ural region, which is an easily accessible part of the mountain range. The Finno-Ugric groups might have settled on both sides of the Urals during the early Medieval period. Archeological records, for example, from central-eastern Uralic site Uelgi, indicate an archaeological cultural mixture of northern Ugric and eastern steppic Turkic elements. These eastern components show cultural connections toward the region of the Emba River in today's western Kazakhstan and toward the Srostki culture, which indicates that the ancient Hungarian population could already have been reached in the Central Ural region by several cultural and genetic influences. Our laboratory studies the genetic composition of the people buried in 7-11th century cemeteries of the Ural region and compares the data with other 7-12th century DNA results from Eurasia.
The latest results of the project can be read in the conference book of the "IV. Early Hungarian History Conference"
Publications of the project:
Csáky Veronika, Gerber Dániel, Szeifert Bea, Egyed Balázs, Stégmár Balázs, Szergej G. Botalov, Ivan V. Grudocsko, Natalja P. Matvejeva, Alekszandr Sz. Zelenkov, Anasztaszija V. Szlepcova, Rimma D. Golgyina, Andrej V. Danics, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Türk Attila, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna: Genetikai adatok az Urál vidék kora középkori temetkezéseiből a korai magyarsággal kapcsolatba hozható régészeti hagyaték tükrében. In Hadak útján - A népvándorláskor fiatal kutatóinak XXIX. konferenciája, Budapest, 2019. november 15-16., 2023. kiad., 4:113–157. Budapest: Bölcsészettudományi Kutatóközpont, Magyar Őstörténeti Kutatócsoport; Pázmány Péter Katolikus Egyetem, Régészettudományi Intézet; Martin Opitz Kiadó.
Csáky Veronika, Gerber Dániel, Csiky Gergely, Koncz István, Szeifert Bea, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Egyed Balázs, Pamjav Horolma, Marcsik Antónia, Molnár Erika, Pálfi György, Gulyás András, Kovacsóczy Bernadett, M. Lezsák Gabriella, Lőrinczy Gábor, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna, Vida Tivadar: Az avar kori elit eredetének és rokoni szerveződésének archeogenetikai vizsgálata. In Hadak útján - A népvándorláskor fiatal kutatóinak XXIX. konferenciája, Budapest, 2019. november 15-16., 2023. kiad., 4:59–78. Budapest: Bölcsészettudományi Kutatóközpont, Magyar Őstörténeti Kutatócsoport; Pázmány Péter Katolikus Egyetem, Régészettudományi Intézet; Martin Opitz Kiadó
Participants of the project: Dr Attila Türk (leader of the project, Péter Pázmány Catholic University), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH), Bea Szeifert (IAG RCH, ELTE), Veronika Csáky (IAG RCH), Dániel Gerber (IAG RCH, ELTE)
Partner institute: Archaeological Department of the Péter Pázmány Catholic University
Genetic investigations of Bronze Age societies
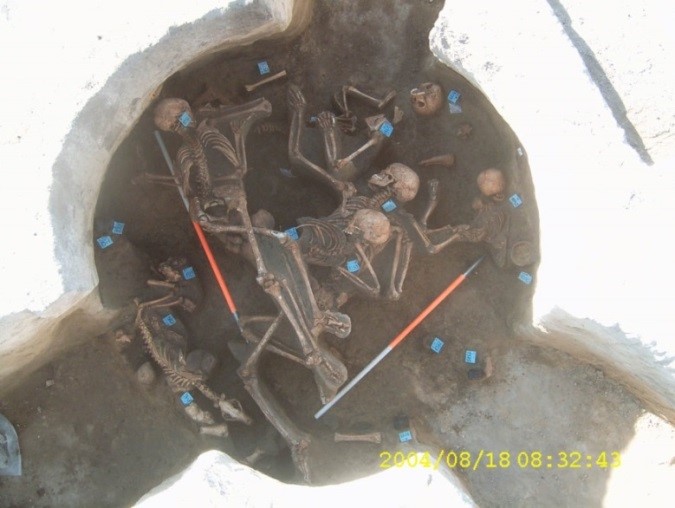 As part of Viktória Kiss' Moment project we investigate Bronze Age multiple inhumations from sites Érd and Balatonkeresztúr in Hungary. Our research focuses are the study of possible kinship relations between the individuals and the molecular pathological screening of the Bronze Age population.
As part of Viktória Kiss' Moment project we investigate Bronze Age multiple inhumations from sites Érd and Balatonkeresztúr in Hungary. Our research focuses are the study of possible kinship relations between the individuals and the molecular pathological screening of the Bronze Age population.
The prehistoric genomic project of the laboratory is now extended with the analyses of further 60 samples from the Middle and Late Bronze Age populations, in collaboration with the Harvard Medical School.
Participants of the project: Viktória Kiss (IAG RCH), Vajk Szeverényi, Gabriella Kulcsár (IA RCH HAS), Kitti Köhler (IAG RCH), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH), Dániel Gerber (IAG RCH, ELTE), Tamás Hajdu (ELTE), Szilvia Fábián (HNM)
Partner institutes:
- Department of Anthropology, Natural History Museum, Budapest
- Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston (Prof. Dr. David Reich)
Publications of the project:
- Interdisciplinary analyses of Bronze Age communities from Western Hungary reveal complex population histories. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2023;, msad182, https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msad182
- Kustár Ágnes, Gerber Dániel, Fábián Szilvia, Köhler Kitti, Mende Balázs Gusztáv, Szécsényi-Nagy Anna, Kiss Viktória: Bronzkori nő szobrászi arcrekonstrukciója Balatonkeresztúr-Réti-dűlő lelőhelyről. Anthropológiai Közlemények (2022. évi kötet) https://ojs.mtak.hu/index.php/anthropkozl?fbclid=IwAR2LGhHRaOtnby2RWuVPGnvec-CWnukOaqpU6f0lPWzR2S2LBgKhNZyo4XA
Mobility and population transformation in the Carpathian Basin during the 5th to 7th centuries AD: changing societies and identities
The interdisciplinary OTKA project (NN 113157) involves the ancient DNA study of ca. 20 individuals, found in preciously furnished graves from the early Avar period. These people, buried with golden or silver embossing swords, could have been the leaders of the inner-Asian or Eastern-European nomad tribe. Based on ethnographic studies, this highest social class of the Avar society was organized by kinship relations. These affiliations are the focus of our genetic study, using well-established archaeogenetic methods, and forensic tools. Studying the early Avar period specimens has a population genetic aspect as well.
Comparing the enlarged Avar mitochondrial DNA dataset to other early medieval ancient DNA results and to the genetic diversity of modern-day Eurasian populations, we will be able to estimate the Inner Asian portion of the Avar (elite) population's genetic variability. We aim to sequence whole mitochondrial genomes with Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) techniques, and a large number of nuclear SNPs (1240k).
Participants: Dr Tivadar Vida (IA RCH HAS), Veronika Csáky (IAG RCH HAS), Dániel Gerber (IAG RCH HAS, FS ELTE), Anna Szécsényi-Nagy (IAG RCH HAS), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH HAS)
Partner institutes:
- Institute of Archaeological Sciences, ELTE University, Budapest
- Department of Biological Anthropology, University of Szeged
- Department of Anthropology, Natural History Museum, Budapest
International partner institute in the project:
- Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, Jena (Prof. Dr. Johannes Krause)
First results about the Inner Asian genetic connections of the Avar period nomadic elite can be read on BioRxiv (2018).
Horse domestication in the Carpathian Basin
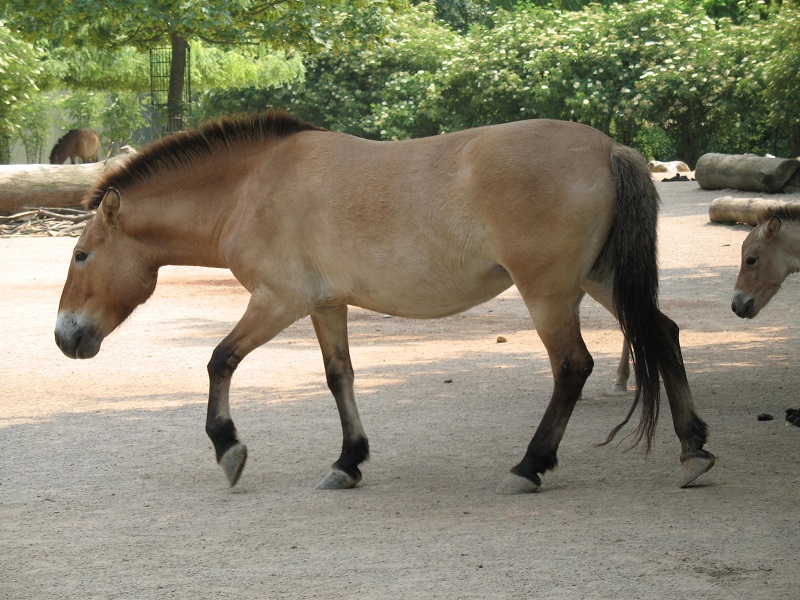 The ERC #681605 project led by Prof. Ludovic Orlando aims to reveal the human-horse relationships in prehistory with special attention to horse domestication. To achieve this, complex and wide genetic analyses are under implementation, where our laboratory takes part in collaboration with the Momentum Mobility Research Group of our institute. The genetic results of the already closed OTKA NF 104792 project led by Dr. Erika Gál are included in this current research.
The ERC #681605 project led by Prof. Ludovic Orlando aims to reveal the human-horse relationships in prehistory with special attention to horse domestication. To achieve this, complex and wide genetic analyses are under implementation, where our laboratory takes part in collaboration with the Momentum Mobility Research Group of our institute. The genetic results of the already closed OTKA NF 104792 project led by Dr. Erika Gál are included in this current research.
Participants of the project: Dániel Gerber (IAG RCH, ELTE), Anna Szécsényi-Nagy (IAG RCH), and the fellow researchers of the Momentum Mobility Research Group
Publications of the project:
- Pablo Librado, Naveed Khan, Antoine Fages, Mariya A. Kusliy, Tomasz Suchan, Laure Tonasso-Calvière, Stéphanie Schiavinato, Duha Alioglu, Aurore Fromentier, Aude Perdereau, Jean-Marc Aury, Charleen Gaunitz, Lorelei Chauvey, Andaine Seguin-Orlando, Clio Der Sarkissian, John Southon, Beth Shapiro, Alexey A. Tishkin, Alexey A. Kovalev, Saleh Alquraishi, Ahmed H. Alfarhan, Khaled A. S. Al-Rasheid, Timo Seregély, Lutz Klassen, Rune Iversen, Olivier Bignon-Lau, Pierre Bodu, Monique Olive, Jean-Christophe Castel, Myriam Boudadi-Maligne, Nadir Alvarez, Mietje Germonpré, Magdalena Moskal-del Hoyo, Jarosław Wilczyński, Sylwia Pospuła, Anna Lasota-Kuś, Krzysztof Tunia, Marek Nowak, Eve Rannamäe, Urmas Saarma, Gennady Boeskorov, Lembi Lōugas, René Kyselý, Lubomír Peške, Adrian Bălășescu, Valentin Dumitrașcu, Roxana Dobrescu, Daniel Gerber, Viktória Kiss, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Balázs G. Mende, Zsolt Gallina, Krisztina Somogyi, Gabriella Kulcsár, Erika Gál, Robin Bendrey, Morten E. Allentoft, Ghenadie Sirbu, Valentin Dergachev, Henry Shephard, Noémie Tomadini, Sandrine Grouard, Aleksei Kasparov, Alexander E. Basilyan, Mikhail A. Anisimov, Pavel A. Nikolskiy, Elena Y. Pavlova, Vladimir Pitulko, Gottfried Brem, Barbara Wallner, Christoph Schwall, Marcel Keller, Keiko Kitagawa, Alexander N. Bessudnov, Alexander Bessudnov, William Taylor, Jérome Magail, Jamiyan-Ombo Gantulga, Jamsranjav Bayarsaikhan, Diimaajav Erdenebaatar, Kubatbeek Tabaldiev, Enkhbayar Mijiddorj, Bazartseren Boldgiv, Turbat Tsagaan, Mélanie Pruvost, Sandra Olsen, Cheryl A. Makarewicz, Silvia Valenzuela Lamas, Silvia Albizuri Canadell, Ariadna Nieto Espinet, Ma Pilar Iborra, Jaime Lira Garrido, Esther Rodríguez González, Sebastián Celestino, Carmen Olària, Juan Luis Arsuaga, Nadiia Kotova, Alexander Pryor, Pam Crabtree, Rinat Zhumatayev, Abdesh Toleubaev, Nina L. Morgunova, Tatiana Kuznetsova, David Lordkipanize, Matilde Marzullo, Ornella Prato, Giovanna Bagnasco Gianni, Umberto Tecchiati, Benoit Clavel, Sébastien Lepetz, Hossein Davoudi, Marjan Mashkour, Natalia Ya. Berezina, Philipp W. Stockhammer, Johannes Krause, Wolfgang Haak, Arturo Morales-Muñiz, Norbert Benecke, Michael Hofreiter, Arne Ludwig, Alexander S. Graphodatsky, Joris Peters, Kirill Yu. Kiryushin, Tumur-Ochir Iderkhangai, Nikolay A. Bokovenko, Sergey K. Vasiliev, Nikolai N. Seregin, Konstantin V. Chugunov, Natalya A. Plasteeva, Gennady F. Baryshnikov, Ekaterina Petrova, Mikhail Sablin, Elina Ananyevskaya, Andrey Logvin, Irina Shevnina, Victor Logvin, Saule Kalieva, Valeriy Loman, Igor Kukushkin, Ilya Merz, Victor Merz, Sergazy Sakenov, Victor Varfolomeyev, Emma Usmanova, Viktor Zaibert, Benjamin Arbuckle, Andrey B. Belinskiy, Alexej Kalmykov, Sabine Reinhold, Svend Hansen, Aleksandr I. Yudin, Alekandr A. Vybornov, Andrey Epimakhov, Natalia S. Berezina, Natalia Roslyakova, Pavel A. Kosintsev, Pavel F. Kuznetsov, David Anthony, Guus J. Kroonen, Kristian Kristiansen, Patrick Wincker, Alan Outram & Ludovic Orlando: The origins and spread of domestic horses from the Western Eurasian steppes. Nature (2021). https:
//doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021- 04018-9
Our research is part of Dr. Erika Gál's OTKA project "From the environment to belief systems: changing lifeways and culture as reflected by animal remains between the Late Copper Age and the Late Bronze Age". We focus on 6-2th millennium BC horse remains from the Carpathian Basin, and investigate coat color markers and mitochondrial genomes of these specimens dated back to the Middle Bronze Age. The genetic results will be implemented to ERC #681605 project lead by Prof. Ludovic Orlando.
Genomic exploration of cultural transformations over 4,000 years of the Carpathian Basin's prehistory
 The research project Genomic Carpathian Prehistory focuses on population transformations in the Carpathian Basin between 6000-2000 BC (from the Early Neolithic to the end of the Early Bronze Age), sampling individuals with cultural assignments from almost every archaeological cultures within the mentioned time interval. The project team intends to study population structure and mixture events, and reconstruct deep population history over 4,000 years of the Carpathian Basin's prehistory. For this purpose, we use next-generation DNA sequencing methods (NGS) on a human genome-scale, with target enrichment (capture) approaches, developed by the team of Prof. Dr. David Reich's laboratory (Harvard Medical School).
The research project Genomic Carpathian Prehistory focuses on population transformations in the Carpathian Basin between 6000-2000 BC (from the Early Neolithic to the end of the Early Bronze Age), sampling individuals with cultural assignments from almost every archaeological cultures within the mentioned time interval. The project team intends to study population structure and mixture events, and reconstruct deep population history over 4,000 years of the Carpathian Basin's prehistory. For this purpose, we use next-generation DNA sequencing methods (NGS) on a human genome-scale, with target enrichment (capture) approaches, developed by the team of Prof. Dr. David Reich's laboratory (Harvard Medical School).
Hungarian colleagues involved in the project: Eszter Bánffy, János Jakucs, Kitti Köhler, Krisztián Oross, Tibor Marton, Anett Osztás, Gabriella Kulcsár, Viktória Kiss, Mária Bondár (IA RCH HAS), Anna Szécsényi-Nagy, Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH HAS).
International partner institutes in the project:
- Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston (Prof. Dr. David Reich)
- Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, Jena (Dr. Wolfgang Haak)
- Institute for Prehistory and Archaeological Science and Hightech Research Center, University of Basel, Basel
- Center of Natural and Cultural History of Teeth, Danube Private University, Krems (Prof. Dr. Kurt W. Alt)
- Roman-Germanic Commission, German Archaeological Institute, Frankfurt (Prof. Dr. Eszter Bánffy)
Historical genetics in the research of the Hungarian ethnogenesis
(in cooperation with the Institute of Genetics, Biological Research Centre HAS, Szeged)
 The primary purpose of this project (in the framework of the 5th NKFP, 2001-2004) was to search for genetic evidence, which could answer archaeological and historical issues, and clarify certain aspects of Central and Eastern European populations' history. The applied molecular genetic analyses allow us to separate the autochthons (indigenous) people from the immigrants of a certain region. On the other hand, it can throw light on the genetic relationships of populations characterized by the archaeological point of view. During our scientific work, archaeologically and anthropologically well-characterized remains were examined for the mitochondrial DNA. Our aim was to study the maternal lineages of the samples and fit them into a historical and archaeological context. We developed a new sampling method, in order to gain not only a large amount of bone powder but also high-quality samples, which were free from modern DNA.
The primary purpose of this project (in the framework of the 5th NKFP, 2001-2004) was to search for genetic evidence, which could answer archaeological and historical issues, and clarify certain aspects of Central and Eastern European populations' history. The applied molecular genetic analyses allow us to separate the autochthons (indigenous) people from the immigrants of a certain region. On the other hand, it can throw light on the genetic relationships of populations characterized by the archaeological point of view. During our scientific work, archaeologically and anthropologically well-characterized remains were examined for the mitochondrial DNA. Our aim was to study the maternal lineages of the samples and fit them into a historical and archaeological context. We developed a new sampling method, in order to gain not only a large amount of bone powder but also high-quality samples, which were free from modern DNA.
Historical genetics of the Carpathian Basin
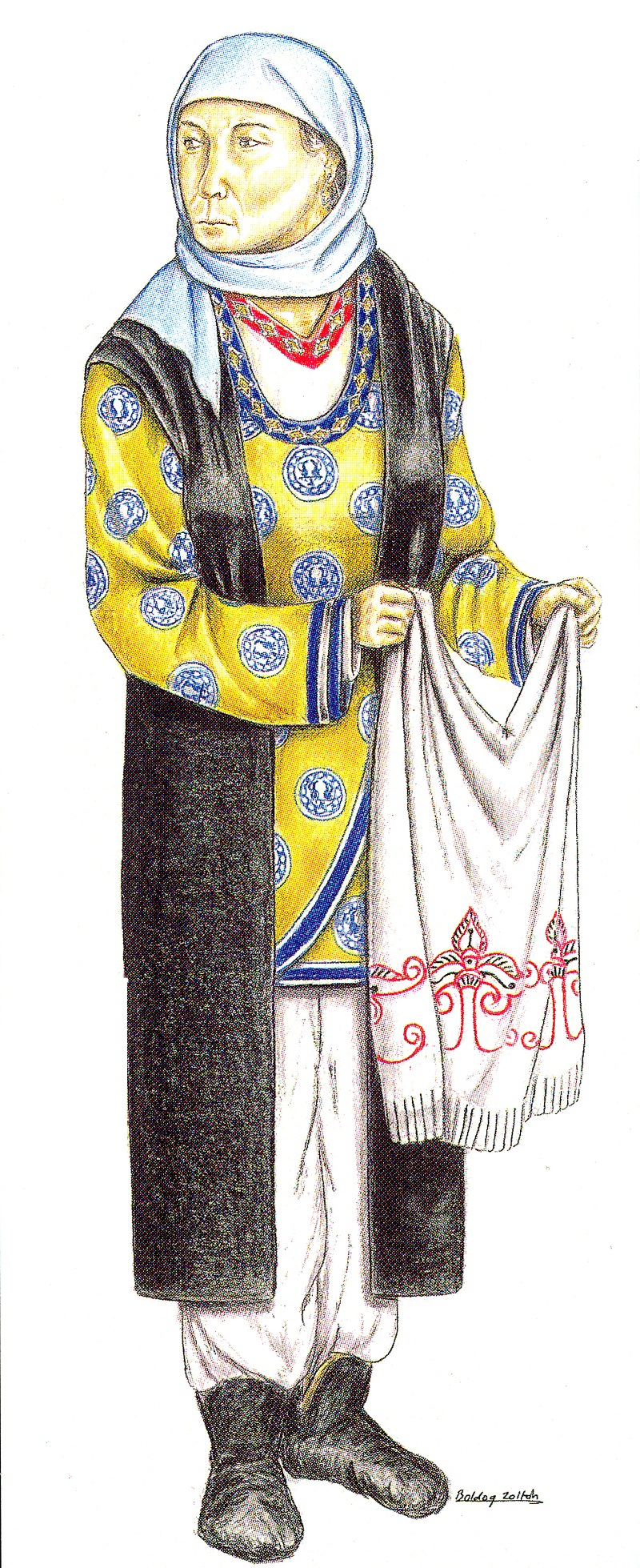 (NKFP 5/038/2004 project, in cooperation with the Institute of Genetics, Biological Research Center HAS, Szeged)
(NKFP 5/038/2004 project, in cooperation with the Institute of Genetics, Biological Research Center HAS, Szeged)
The former research project of the Hungarian ethnogenesis run parallel in Szeged and Budapest between 2004-2007. We aimed to involve such specimens in the project, which help to answer smaller and independent archaeological research questions (e.g. Harta-Freifelt cemetery). On the other hand, we also tried to collect samples from the whole Carpathian Basin, concentrating on the Hungarian Conquest and the early Arpad age (9-12th AD) periods.
Participants of the project: Prof. Dr István Raskó, Gyöngyvér Tömöry, Erika Bogácsi-Szabó, Bernadett Csányi (IG BRC HAS, Szeged), Aranka Csősz, Péter Langó (IA RCH HAS), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH HAS).
The results of the two NKFP projects were summarized in the issue of October 2008 of the 'Hungarian Science' journal (Magyar Tudomány). Webpage of the journal Hungarian Science. Further papers are found under 'Publications' on our webpage.
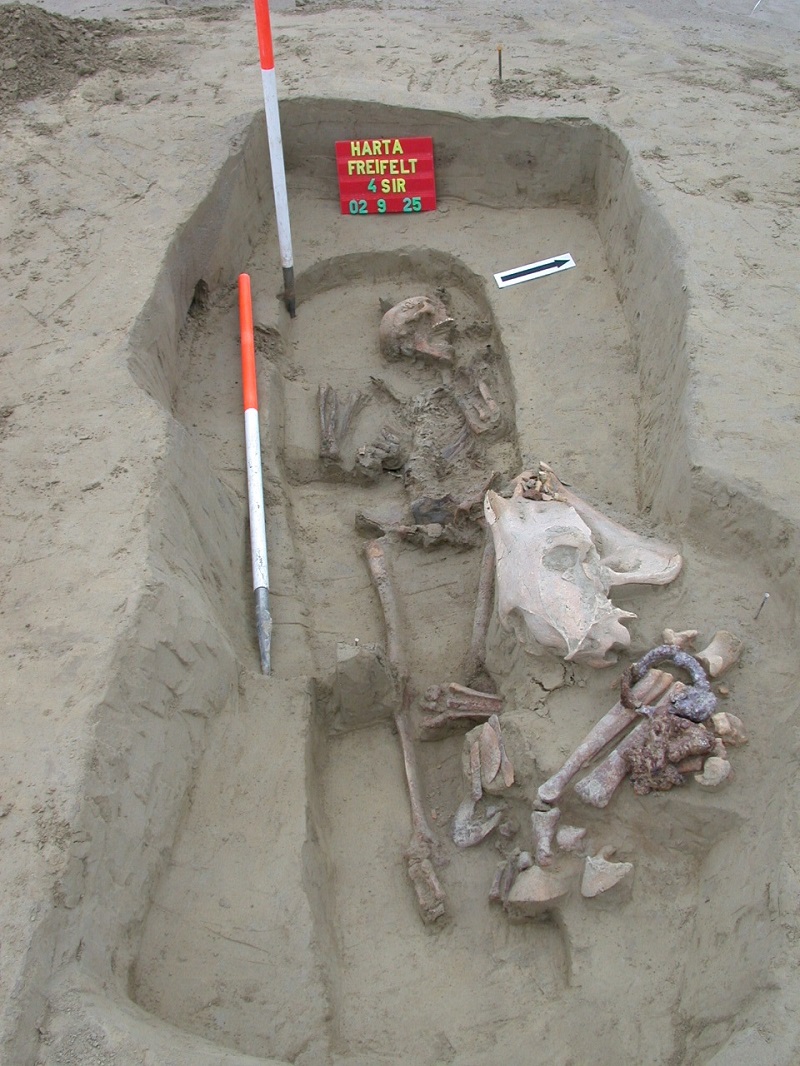
Archaeogenetic analysis of the Hungarian Conquest period cemetery Harta-Freifelt (10th century AD)
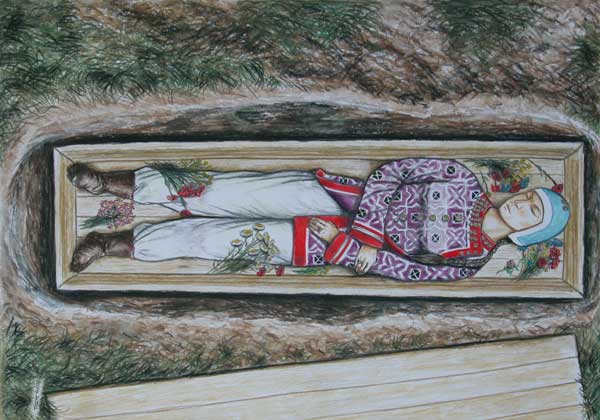 The archaeogenetic analysis of the Harta cemetery was part of the former 'NKFP' projects, focusing on the 9-10th century period of the Carpathian Basin. Harta-Freifelt is a completely excavated and genetically investigated classic Hungarian Conquest period cemetery. The mitochondrial DNA analyses did not reveal any maternal kinship connection, which was a surprising result, regarding that more than 80% of the buried individuals were women. This study can imply a new social model for the small Conquest period graveyards, which have been interpreted yet as family burial sites.
The archaeogenetic analysis of the Harta cemetery was part of the former 'NKFP' projects, focusing on the 9-10th century period of the Carpathian Basin. Harta-Freifelt is a completely excavated and genetically investigated classic Hungarian Conquest period cemetery. The mitochondrial DNA analyses did not reveal any maternal kinship connection, which was a surprising result, regarding that more than 80% of the buried individuals were women. This study can imply a new social model for the small Conquest period graveyards, which have been interpreted yet as family burial sites.
Participants of the research: Prof. Dr István Raskó, (IG BRC HAS, Szeged), Aranka Csősz (IA RCH HAS), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH HAS), Péter Langó (IA RCH HAS).
Archaeogenetic analysis of Avar period (6-7th century AD) burials from the Carpathian Basin
The Szegvár-Oromdűlő early Avar period cemetery and the burial custom of catacomb graves east of the Tisza River in Hungary (OTKA- 91183 project)
Our archaeogenetic analyses were part of an interdisciplinary OTKA project, led by the Móra Ferenc Museum, Szeged (Lívia Bende, Gábor Lőrinczy) between 2009 and 2012. The aim of the project was to detect potential population history events behind the changes of burial customs of catacomb type graves in the former Avar territory east of river Tisza between rivers Körös and Maros. Three archaeological sites were partially sampled and analyzed: Szegvár-Oromdűlő, Székkutas-Kápolnadűlő, Pitvaros-Víztározó. The skeletal remains were in a very bad state of preservation for ancient DNA, therefore the repeated analyses only obtained sufficiently reproduced DNA sequences in the HVS-I region of the mitochondrial DNA in 34 cases. These results can be the basis of a future Avar period mtDNA dataset, but they are too scarce to evaluate independently.
The Avar mtDNA dataset was part of the Conquest-period study of our team: Csősz, A, Szécsényi-Nagy, A, Csákyova, V, Langó, P, Bódis, V, Tömöry, G, Nagy, M, Mende, BG. (2016) Maternal Genetic Ancestry and Legacy of 10th Century AD Hungarians. BioRxiv. 10.1101/056655
Eastern connections of the Hungarian Conquest period archaeological remains in the context of the Hungarian prehistory
Archaeological database and archaeometric researches (OTKA -106369 project)
 The ancient Hungarians originated from the Ural region in today's central Russia and migrated across the Eastern European steppe, according to historical sources. The historically and linguistically assumed homeland of the ancient Hungarians was in the Central Ural region, which is an easily accessible part of the mountain range. The Finno-Ugric groups might have settled on both sides of the Urals during the early Medieval period. Archeological records, for example, from central-eastern Uralic site Uelgi, indicate an archaeological cultural mixture of northern Ugric and eastern steppic Turkic elements. These eastern components show cultural connections toward the region of the Emba River in today's western Kazakhstan and toward the Srostki culture, which indicates that the ancient Hungarian population could already have been reached in the Central Ural region by several cultural and genetic influences. Our laboratory studies the genetic composition of the people buried in 7-11th century cemeteries of the Ural region and compares the data with other 7-12th century DNA results from Eurasia.
The ancient Hungarians originated from the Ural region in today's central Russia and migrated across the Eastern European steppe, according to historical sources. The historically and linguistically assumed homeland of the ancient Hungarians was in the Central Ural region, which is an easily accessible part of the mountain range. The Finno-Ugric groups might have settled on both sides of the Urals during the early Medieval period. Archeological records, for example, from central-eastern Uralic site Uelgi, indicate an archaeological cultural mixture of northern Ugric and eastern steppic Turkic elements. These eastern components show cultural connections toward the region of the Emba River in today's western Kazakhstan and toward the Srostki culture, which indicates that the ancient Hungarian population could already have been reached in the Central Ural region by several cultural and genetic influences. Our laboratory studies the genetic composition of the people buried in 7-11th century cemeteries of the Ural region and compares the data with other 7-12th century DNA results from Eurasia.
The latest results of the project can be read in the conference book of the "IV. Early Hungarian History Conference"
Participants of the project: Dr Attila Türk (leader of the project, Péter Pázmány Catholic University), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH HAS), Bea Szeifert (IAG RCH HAS, FS ELTE), Veronika Csáky (IAG RCH HAS), Dániel Gerber (IAG RCH HAS, FS ELTE)
Partner institute: Archaeological Department of the Péter Pázmány Catholic University
Genetic analyses of the 13. grave group at Alsónyék 10b site
Alsónyék: from the beginnings of the food production until the end of the Late Neolithic (OTKA-81230 project, led by Prof. Dr. Eszter Bánffy)
The 13. grave group at Alsónyék 10b site within a large site complex is assigned to the Late Neolithic (5th millennium BC) Lengyel culture. We analyzed and typed the mtDNA of 36 individuals buried in this area. Besides the maternal lineages, we also searched for genetic traces of the pathogen Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in the skeletal remains of 38 Late Neolithic individuals. The results are reported in the June 2015 issue of the Tuberculosis journal.
Click here for redirecting to the webpage of Tuberculosis.
Participants of the project: Dr Eszter Bánffy, Anett Osztás, Aranka Csősz, Kitti Köhler, Balázs G. Mende, (IAG RCH HAS), Annamária Pósa, Dr György Pálfi (University of Szeged)
Partner institutes:
- Department of Biological Anthropology, University of Szeged
- Institute for Mummies and the Iceman, EURAC Research, Bolzano
The population history of the Carpathian Basin in the Neolithic period and its influence on the colonization of Central Europe
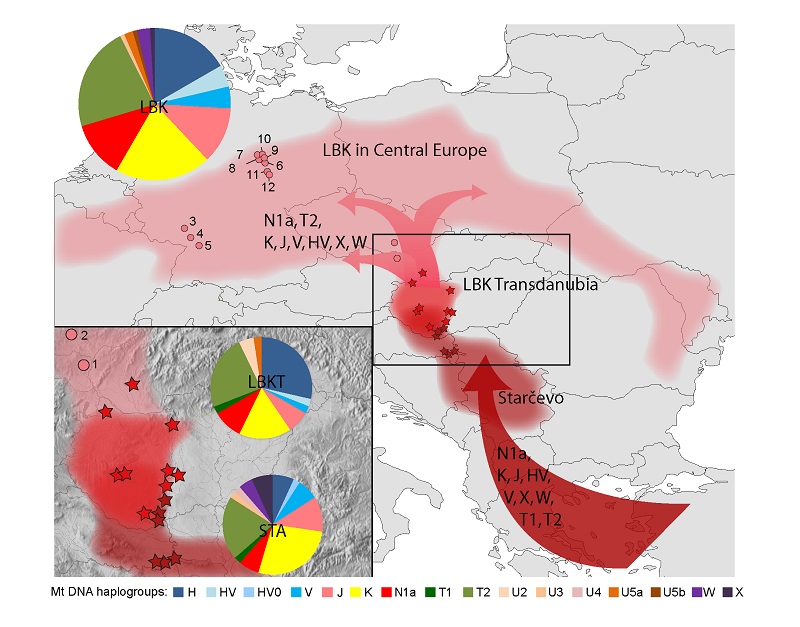 This interdisciplinary project was funded by the German Research Foundation (project number: AI 287/10-1) between 2010 and 2014. The original project title was 'Bevölkerungsgeschichte des Karpatenbeckens in der Jungsteinzeit und ihr Einfluss auf die Besiedlung Mitteleuropas'. Prof. Dr. Kurt W. Alt (Johannes Gutenberg University) and Prof. Dr. Eszter Bánffy (IA RCH HAS) were the organizers and initiators of the project. 2000 years of population history in the Carpathian Basin was studied by bioarchaeological methods, and the results were compared with other European prehistoric data. We sampled human remains from ca. 600 Neolithic and Copper Age burials and analyzed them under the scientific aspects of archaeology, anthropology, molecular genetics, and stable isotope (geochemistry) studies. Our aims were to examine the Neolithic diet, lifestyle, mobility and genetic relationships of the people ordered into geographically and/or chronologically distinctive archaeological cultures. The results also helped us reconstructing the Neolithic people's dispersal, population dynamic, and connection systems.
This interdisciplinary project was funded by the German Research Foundation (project number: AI 287/10-1) between 2010 and 2014. The original project title was 'Bevölkerungsgeschichte des Karpatenbeckens in der Jungsteinzeit und ihr Einfluss auf die Besiedlung Mitteleuropas'. Prof. Dr. Kurt W. Alt (Johannes Gutenberg University) and Prof. Dr. Eszter Bánffy (IA RCH HAS) were the organizers and initiators of the project. 2000 years of population history in the Carpathian Basin was studied by bioarchaeological methods, and the results were compared with other European prehistoric data. We sampled human remains from ca. 600 Neolithic and Copper Age burials and analyzed them under the scientific aspects of archaeology, anthropology, molecular genetics, and stable isotope (geochemistry) studies. Our aims were to examine the Neolithic diet, lifestyle, mobility and genetic relationships of the people ordered into geographically and/or chronologically distinctive archaeological cultures. The results also helped us reconstructing the Neolithic people's dispersal, population dynamic, and connection systems.
Co-workers in the project: Prof. Dr Eszter Bánffy, János Jakucs , Kitti Köhler, Krisztián Oross, Tibor Marton, Anett Osztás (IA RCH HAS), Balázs G. Mende, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy (IAG RCH HAS) International co-workers: Prof. Dr Kurt W. Alt, Victoria Keerl, Marc Fecher (Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz)
Partner institutes in the project: Department of Biological Anthropology of the University of Szeged, Institute of Archaeological Sciences of the Eötvös Loránd University, Móra Ferenc Museum, National Heritage Protection Centre of the Hungarian National Museum, Balaton Museum, Biology Department, University of West Hungary, Laczkó Dezső Museum, Damjanich János Museum, Déri János Museum, Dobó István Museum, Herman Ottó Museum, Janus Pannonius Museum, Szent Istvám Király Museum, Wosinsky Mór Museum, Anthropological Center, Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Curt-Engelhorn-Centre for Archaeometry, German Archaeological Institute, Roman-Germanic Commission, and many others.
Archaeogenetic analyses of Nitra-Sindolka cemetery (10-11th century) in Slovakia
The genetic analyses of the 10-11th century cemetery at Nitra-Sindolka were performed in the framework of a three-year scientific research project (VEGA-1/0897/12, Archeogenetický výskum kontaktnej zóny z 10. storočia na Slovensku/Archaeogenetic investigation of a population from the 10th century contact zone).
The research is based on the scientific agreement of four institutions:
- Univerzita Konstantína Filozofa v Nitre (Constantine the Philosopher University in Nitra)
- Institute of Archaeology, RCH HAS, Budapest
- Institute of Archaeology, Slovakian Academy of Science, Nitra
- Janos Selye University, Komarno
The 300 graves of the cemetery were excavated by Dr. Gabriel Fusek in 1985-1986. The site encompasses two areas, which were the burial places of the Hungarian-Slavic mixed plebeian population of the region (so-called Bjelo Brdo culture). During our investigation, we managed to type the mtDNA HVS-I region and assign it to certain mtDNA haplogroups in 14 cases out of the sampled 20 individuals. We compared the results both with our Hungarian Conquest Period dataset and with the European medieval datasets, in order to learn and interpret the genetic composition of a mixed population in the 10-11th century Carpathian Basin.
Leaders of the project: Prof. Dr. Maria Bauerová (Constantine the Philosopher University), Dr. Melinda Nagy (Janos Selye University).
Co-workers in the project: Veronika Csáky (Constantine the Philosopher University) (IAG RCH HAS), Balázs G. Mende (IAG RCH HAS), Aranka Csősz (IA RCH HAS)
Publication of the research: Csákyova V, Szécsényi-Nagy A, Csősz A, Nagy M, Fusek, G, Langó P, Bauer, M, Mende BG, Makovický, P, Bauerová, M. (2016): Maternal Genetic Composition of a Medieval Population from a Hungarian-Slavic Contact Zone in Central Europe. PLoS ONE 11(3): e0151206. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0151206.
Genetic analyses of the individuals, buried into the Rákóczi vault in Košice (Slovakia)
Francis I. Rákóczi was buried in a vault of the Premonstratensian, earlier Jesuit church in Košice. The vault was plundered and wasted repeatedly. The skeletal remains need to be identified and authenticated through the historically documented kinship connections.
Participants of the project: Dr Melinda Nagy (János Selye University), Balázs G. Mende, Anna Szécsényi-Nagy (IAG RCH HAS)



