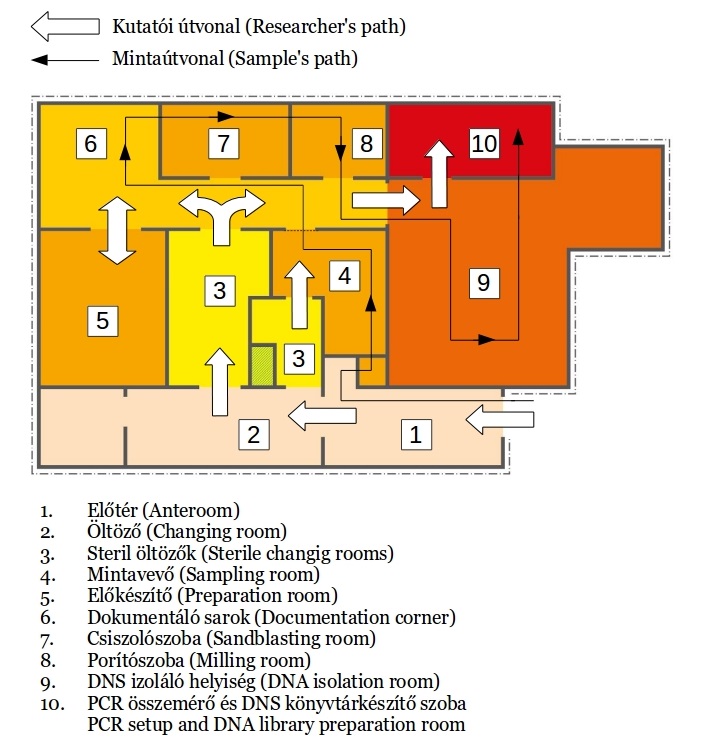
 While most modern DNA molecules exist as long intact strands, ancient DNA is typically damaged, enriched in deaminations, and fragmented into small pieces. The primary objective of an ancient DNA facility is to prevent contamination with modern nucleic acids. This is especially critical for the analysis of human samples, where the risk of contamination by laboratory personnel, museum staff, or archaeological and anthropological colleagues is particularly high. Strict separation between pre- and post-PCR work phases is crucial to prevent the transfer of modern DNA molecules from the post-PCR to the pre-PCR laboratory. To mitigate this risk, the two laboratories are located on separate floors.
While most modern DNA molecules exist as long intact strands, ancient DNA is typically damaged, enriched in deaminations, and fragmented into small pieces. The primary objective of an ancient DNA facility is to prevent contamination with modern nucleic acids. This is especially critical for the analysis of human samples, where the risk of contamination by laboratory personnel, museum staff, or archaeological and anthropological colleagues is particularly high. Strict separation between pre- and post-PCR work phases is crucial to prevent the transfer of modern DNA molecules from the post-PCR to the pre-PCR laboratory. To mitigate this risk, the two laboratories are located on separate floors.
The main parts of the laboratory:
 Ancient DNA clean rooms (pre-PCR laboratory)
Ancient DNA clean rooms (pre-PCR laboratory)
Access to the ancient DNA clean laboratory involves passing through three changing rooms, where researchers change into specialized attire including bodysuits, gloves, specific shoes, face masks, and hairnets. The storage room also houses laboratory supplies. Every item entering the clean rooms undergoes thorough washing with bleach (sodium hypochlorite - NaClO) followed by UV-C irradiation.
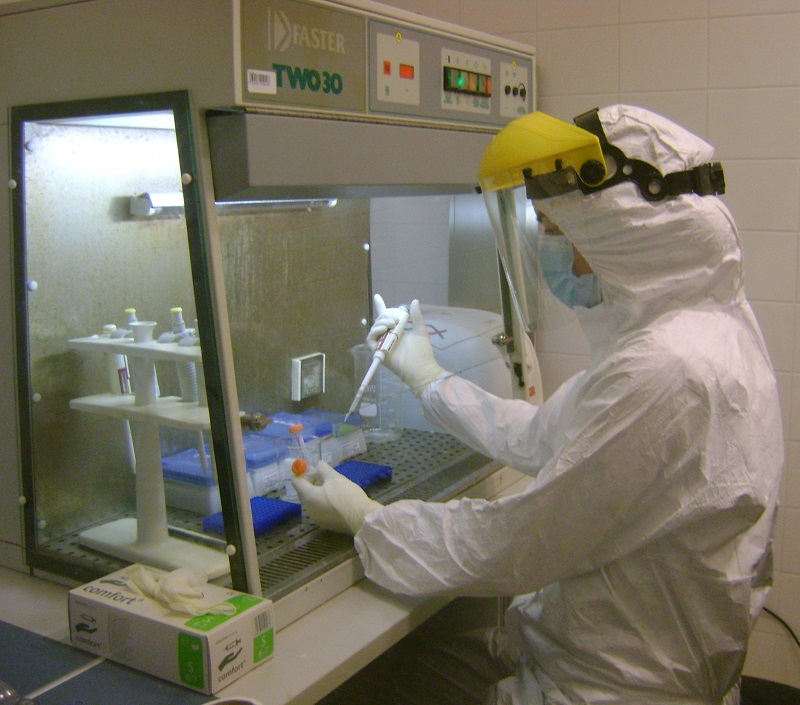
 No modern DNA work is conducted in the pre-PCR laboratory. Work surfaces, reagents, and equipment are routinely irradiated and cleaned with bleach to eliminate any modern DNA contamination. The sample preparation room features a dedicated isolated cabin for the primary cleaning, cutting, and polishing of samples, along with a vacuum system. The cleanrooms of the laboratory are maintained at positive air pressure, ensuring a consistent pressure gradient throughout the facility, with the highest pressure in the DNA extraction room. This room is equipped with a laminar flow hood for conducting DNA extraction procedures. Additionally, a separate preparatory room is equipped with a fume hood for handling reagents, especially those that may be toxic. We utilize HPLC-grade water for reactions and ultrapure water for cleaning purposes.
No modern DNA work is conducted in the pre-PCR laboratory. Work surfaces, reagents, and equipment are routinely irradiated and cleaned with bleach to eliminate any modern DNA contamination. The sample preparation room features a dedicated isolated cabin for the primary cleaning, cutting, and polishing of samples, along with a vacuum system. The cleanrooms of the laboratory are maintained at positive air pressure, ensuring a consistent pressure gradient throughout the facility, with the highest pressure in the DNA extraction room. This room is equipped with a laminar flow hood for conducting DNA extraction procedures. Additionally, a separate preparatory room is equipped with a fume hood for handling reagents, especially those that may be toxic. We utilize HPLC-grade water for reactions and ultrapure water for cleaning purposes.- Post-PCR laboratories
The post-PCR laboratory consists of two departments. One department comprises a semi-clean room for DNA library handling and a dedicated sequencing roo
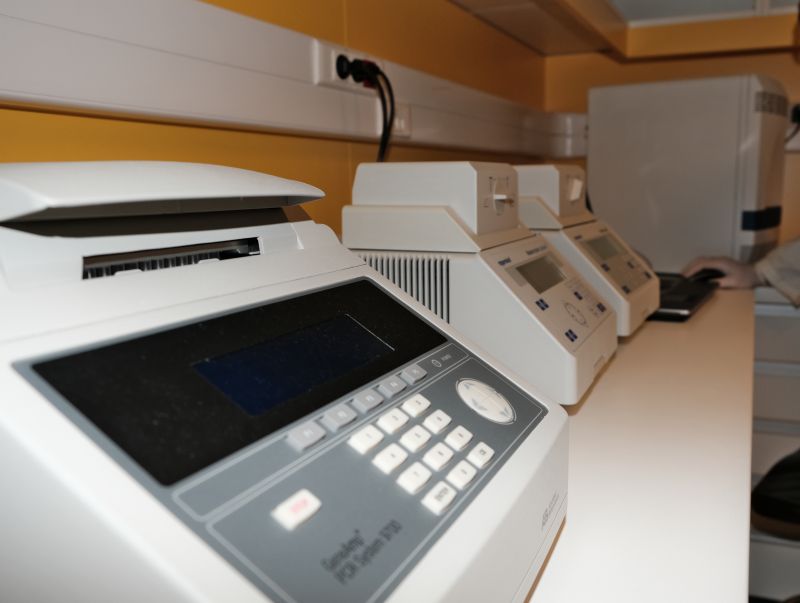 m, while the other sector is utilized for post-PCR analyses. The latter is equipped with thermocyclers, electrophoresis equipment, and gel documentation systems. PCR reactions set up in the clean rooms are transferred to the post-PCR lab for amplification and preparation for downstream analyses. Additionally, the post-PCR laboratory features an extra clean bench specifically designated for hybridization capture reactions. This section of the lab is also utilized for the extraction, amplification, and sequencing of modern DNA samples. To prevent cross-contamination, workflow and sample treatment are strictly segregated between pre-PCR and post-PCR stages. Researchers at the Institute of Archaeogenomics are capable of processing and sequencing highly degraded DNA samples (refer to Chapter Methods for more details).
m, while the other sector is utilized for post-PCR analyses. The latter is equipped with thermocyclers, electrophoresis equipment, and gel documentation systems. PCR reactions set up in the clean rooms are transferred to the post-PCR lab for amplification and preparation for downstream analyses. Additionally, the post-PCR laboratory features an extra clean bench specifically designated for hybridization capture reactions. This section of the lab is also utilized for the extraction, amplification, and sequencing of modern DNA samples. To prevent cross-contamination, workflow and sample treatment are strictly segregated between pre-PCR and post-PCR stages. Researchers at the Institute of Archaeogenomics are capable of processing and sequencing highly degraded DNA samples (refer to Chapter Methods for more details).
Selection of Laboratory Equipment:

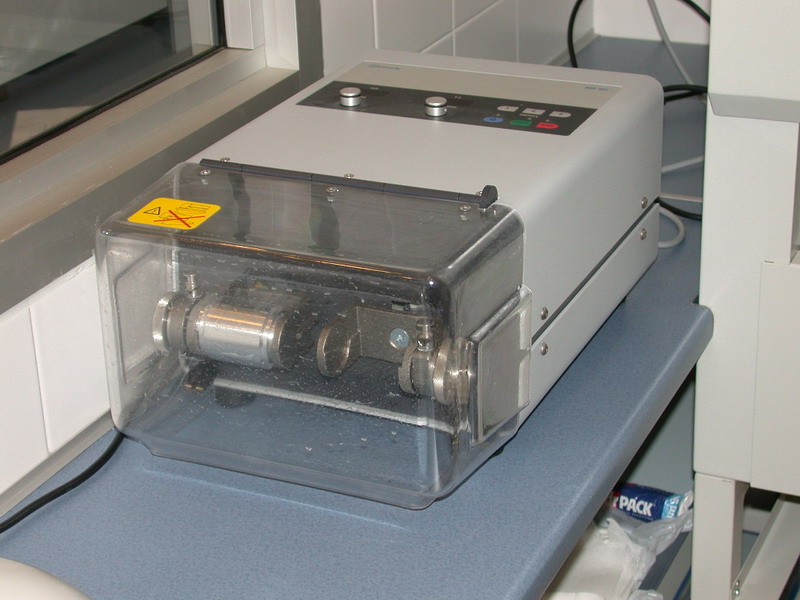
- Sandblasting tools
- Retsch mixer mill
- Laminar flow cabinets and PCR workstations
- PCR equipment, centrifuges, rotators, hybridization chamber, Eppendorf thermal cyclers
- Merck Millipore vacuum filtration system
- Real-time PCR system 7500 (Applied Biosystem)

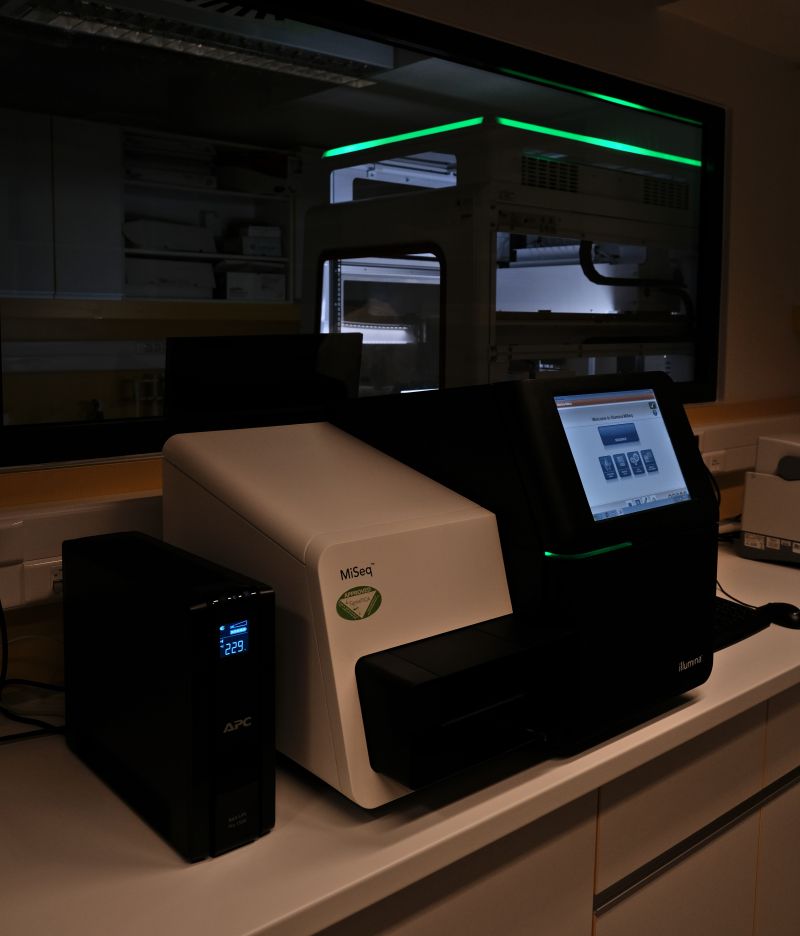
- Illumina MiSeq sequencer
- TapeStation 4200 System (Agilent Genomics)
- Qubit fluorometer
- Vision Express gel documentation system
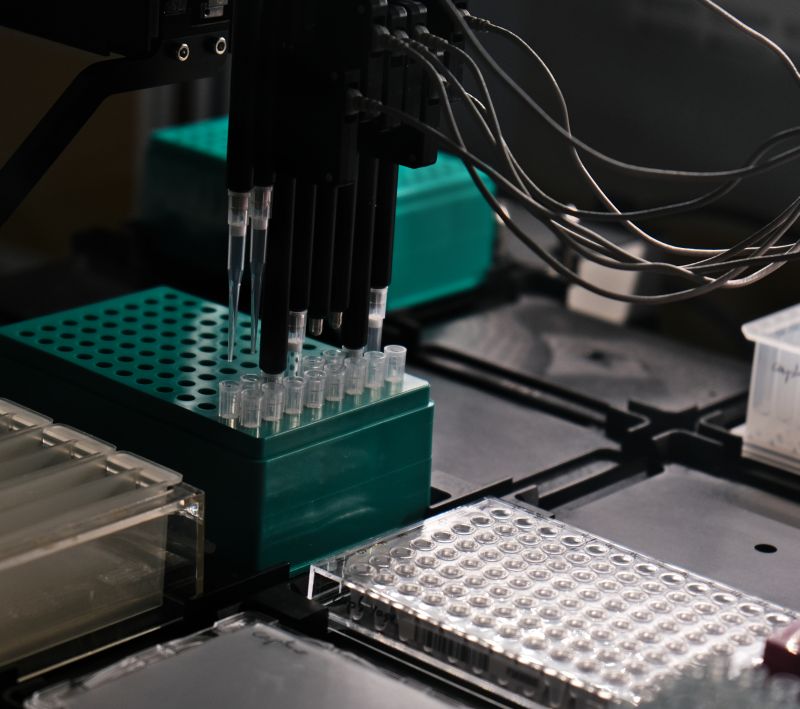
- Beckmann Coulter Biomek i5 robots
If you are interested in collaborating with us, please contact our laboratory chief for further details.



